Tel: +86-134-31394972
E-mail: sales@pre-webguidesystem.com
Tel: +86-134-31394972
E-mail: sales@pre-webguidesystem.com
First, select the tension controller
1. Control method. The ratio of the difference between the two groups of rollers is called the drawing ratio, and the delay rate shown in Fig. 2 can be expressed by the following formula.
D=(v1=v2)/v2
Where D is the draw ratio;
Vl and v2 - the conveying speed of the workpiece on each drum.
The tension of the workpiece between the two sets of rollers with drawing is
T=ES(v1-v2)/v2=ESD
Where T is the tension (N);
E——elastic coefficient of the workpiece (N/mm2):
S——The cross-sectional area of the workpiece (mm2).
It can be seen that the pulling force and the drawing rate are in a share. However, for a workpiece with a large modulus of elasticity, the change in draw is small, and the ambient temperature, moisture content, and thickness inequality factors will cause a large change in tension, so it is not very useful. Regarding materials with a small modulus of elasticity like tires, the control contrast is simply completed when requesting a certain tension and a certain elongation. Figure 3 shows an example of the pull control.
2. Request for selection of the drive. In order to improve the tension accuracy, it is necessary to improve the drawing accuracy, that is, to improve the speed regulation accuracy of the two motors. In order to improve the accuracy, the inverter with speed response control should be selected. In particular, the frequency converter 2 should have a braking function and supply braking torque in a timely manner.
Second, the control method, the torque controller as the control signal tension controller system schematic. The workpiece is moved by the drum 1, and a torque opposite to the direction of rotation is applied to the drum 2, so that the workpiece between the two sets of rollers has a tension which is proportional to the braking torque of the motor of the drum 2. Therefore, the inverter 1 can select the general-purpose inverter to adjust the speed; and the inverter 2 needs to use the vector-controlled inverter with the torque control function.
Request for the drive selection. It is necessary to note that when the workpiece is suddenly cracked, the unloading of the drum 2 will accelerate in the reverse direction and there is a risk of overspeed, so it is necessary to use a frequency converter with a speed limit function. In addition, when the repair and processing operations are performed, the conveyor belt is requested to operate at a lower speed, so the inverter 2 should be provided with a low speed jog function.
Third, the tension controller using the tension checker
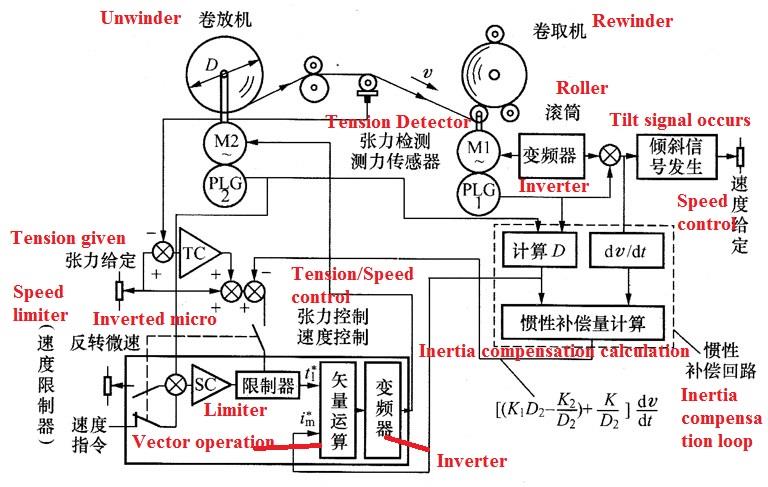
2. Planning key. The paper machine tension controller system in this example has a large mechanical inertia of the winder, so when the coiler accelerates and decelerates, the winder will change the tension due to its own CD2. Although the tension response control can recover to normal tension, the tension that is too large in the transition process will affect the quality of the product, which is not allowed. In order to avoid such shaking, the torque of the motor should be reduced according to the inertia torque corresponding to CD2 when accelerating, and increased when decelerating. This feedforward compensation torque is used to reduce the load on the torque maneuver TC. This kind of compensation is also called inertia compensation, and it has nothing to do with the use of the tension checker.
In addition, the winding machine gradually decreases in diameter as time goes by. At this time, the rotation speed should be changed synchronously to maintain the tension and speed of the control paper, and the constant frequency output characteristic is required for the frequency conversion.
1. Control method. Regarding the high-precision tension controller or the use of the conditioning roller, the reaction of the tension checker can be selected in the case where the control quality has a great influence on the quality of the product. The tension checker has a differential transmitter type and a load cell type. Figure 6 is a diagram of the tension controller of the final process of the paper mill, using the tension checker for the coiler and the winder. The system requests that the paper that has been wound on the reel (roller) be again rolled up from the reel at a high quality with a steady tension. The motor driven by the coiler takes up the paper at a constant speed, and the motor of the winder works with the tension in the regenerative braking state. The drum work of the coiler is independent of the tension controller, so the following is only the main point of the winder. The winder uses a vector-controlled inverter with regenerative work function, and uses a transfer switch to select a tension controller or speed control. Speed control is only used when the paper is punched through, and the tension controller is used for normal work. The speed manipulator SC inputs the speed command and the swivel micro-speed command, so the input of the SC is always given by the deviation method. Using the tension given signal to condition the output limiter of the SC, the actual torque command value can be increased or decreased. In the steady state, the value of the limiter is corrected by the torque manipulator IC input end comparing the tension given and the tension reaction value, and the control effect is to make the two flat. This system adopts this structure method, because the rotation speed of the winding machine does not exceed the micro speed of the rotation, and even if the paper breaks during the winding process, it will not work at over speed.
Fourth, select the tension controller of the conditioning roller
1. Control method. Figure 4 is a schematic illustration of a conditioning roller unit. The conditioning roller uses a tension spring, air pressure, and heavy squeezing force to apply a certain amount of force in a certain direction, regardless of whether the orientation is constant or not, so that the workpiece maintains a certain tension. When the conditioning roller is used, the tension is not directly related to the operation of the inverter, but the resistance supplied is half the size of F. The tension controller function of the conditioning roller is limited to within its allowable stroke.
An example of a tension controller using a conditioning roller. The synchronizing signal machine mounted on the conditioning roller converts the displacement amount against the base orientation into an electric signal and takes it out, and applies it as a compensation signal to the frequency converter 1 as a frequency command. When the conditioning roller is shifted upward, the polarity of the signal should be The speed of the drum 1 is lowered; otherwise, the speed is increased when it is shifted downward. In this way, the conditioning roller is manipulated at the base orientation of the stroke. The advantage of this control method is that the vibration error can be absorbed on the mechanical side, so the general frequency converter can be manipulated with a simple V/F to form the control system.
2. Planning key. This method gives full play to the advantages of the mechanical side to absorb errors in the transition process, and can perform synchronous acceleration and deceleration in a short time without disorderly control. However, depending on the size of the absorption error, the stroke of the conditioning roller is also increased.
In addition, compared with other tension controller methods, the control of the tension cannot be made by electrical means, and it is necessary to adjust it by mechanical means such as spring pressure or air pressure.