Tel: +86-134-31394972
E-mail: sales@pre-webguidesystem.com
Tel: +86-134-31394972
E-mail: sales@pre-webguidesystem.com
The difference between the drive roller and the idler:
Drive rollers and idlers are two other types of rollers commonly used in logistics conveying systems, and their main difference from load-bearing idlers and return idlers is their function and installation location.
1) Drive roller
The driving roller refers to the roller installed at the head or tail of the conveyor to drive the movement of the conveyor belt. Its main function is to drive the movement of the conveyor belt through the transmission device, so as to realize the continuous transportation of goods.
The driving roller usually adopts motors, reducers and other transmission devices, and its number and spacing will also vary due to different conveying requirements. The surface of the drive roller is also treated with paint and other treatments to improve its corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
2) Idlers
Idlers are rollers that are installed at the bottom or side of a conveyor to support the conveyor belt. Its main function is to support the conveyor belt to prevent it from sagging or displacement, and it can also play a role in reducing the friction of the conveyor belt and reducing energy consumption.
Idlers are usually made of steel tubes or plates, and their number and spacing can vary depending on the conveying requirements. The surface of the roller is also treated with paint, etc., to improve its corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance.
In general, load-bearing rollers (sometimes referred to as troughed rollers) support the conveyor belt that carries the material, while return rollers are used to support the no-load conveyor belt; Whereas, the drive roller is mainly used to drive the conveyor belt. They perform their duties in the logistics transportation system and cooperate with each other to jointly realize the efficient transportation of goods.
The difference between load-bearing rollers and return rollers:
1) Bearing rollers
Load-bearing rollers refer to rollers used to support and carry goods, which are usually installed at the bottom or side of the conveyor. The main function of the load roller is to transport the goods from the starting point to the end point, and by cooperating with the transmission device, continuous conveying can be realized.
The load-bearing roller is usually made of steel pipe or steel plate, and the surface is usually galvanized, painted and other treatments to improve its corrosion resistance and wear resistance. The number and spacing of the rollers can also vary depending on the conveying requirements.
2) Return rollers
Return rollers are rollers that are installed at the bottom or side of the conveyor to support and recycle the conveyor belt. Its main function is to support the conveyor belt to prevent it from sagging or displacement, and it can also play a role in reducing the friction of the conveyor belt and reducing energy consumption.
The return rollers are usually made of steel tubes or plates, and their number and spacing can vary depending on the conveying requirements. The surface of the return roller is also treated with paint and other treatments to improve its corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Belt conveyor idlers are classified as follows:
1) Trough idlers
Trough idlers are divided into two types: bracket type and hanging type, and the commonly used groove angle is 30° and 35°. It is used for belt conveyors to carry branches, support the conveyor belt and the materials on it.
2) Parallel rollers
Parallel idlers are divided into parallel upper idlers and parallel lower idlers. Parallel upper rollers are used to carry branches, support conveyor belts and the goods on them; Parallel lower idlers are used for the return branch and support the conveyor belt.
3) Forward tilting rollers
Forward tilt rollers are divided into trough forward tilt rollers and V-shaped forward tilt rollers. Trough forward rollers are used for the load branch, and V-shaped forward rollers are used for the return branch, and they have the effect of correcting belt mistracking. The forward angle is usually 1°-3°.
4) Self-aligning rollers
Self-aligning rollers are divided into friction upward aligning rollers, tapered upward aligning rollers, friction upward leveling self-aligning rollers, friction downward aligning rollers and tapered downward aligning rollers. It is used for load-bearing branches or return branches, and has the effect of correcting conveyor belt mistracking.
5) Buffer rollers
The buffer roller is used at the receiving place of the conveyor to reduce the impact of the material on the conveyor belt and prolong the service life of the conveyor belt. There are two kinds of buffer rollers: rubber ring type and spring plate type, and the common groove angle is 30° and 35°.
6) Return rollers
Return rollers are used for return branching and are available as parallel lower rollers, V-shaped rollers, reverse V-shaped rollers, comb rollers and spiral rollers. The use of V-shaped and inverse V-shaped idlers is effective in preventing belt mistracking, and comb idlers and spiral idlers remove material stuck to the belt.
7) Transition rollers
Transition rollers are used between the roller and the first set of standard rollers to gradually form a groove or expand from the groove to a flat shape, so as to reduce the additional stress on the edge of the conveyor belt and prevent the phenomenon of spilling when the belt is spreading. There are several types of groove angles: 10°, 20° and 30°.
In the actual use process, according to the different types and functions of various idlers, in order to maximize the efficiency of the belt conveyor.
Significance of determining the spacing of idlers in a belt conveyor:
The increase in the number of idlers not only increases the huge investment, but also increases the running resistance of the conveyor, resulting in an increase in the size of the conveyor belt and the power of the motor. Through the reasonable determination and optimal arrangement of the roller spacing of the belt conveyor, the amount of rollers can be greatly reduced, and its advantages are very obvious. If the number of rollers is halved, the equipment investment will be significantly reduced. The number of idlers is reduced, so that the running resistance of the conveyor is reduced, the power consumption is reduced, and the electric energy is saved. Due to the large amount of idler rollers used in the belt conveyor, it is prone to failure. Therefore, the reasonable arrangement of the idler reduces the amount of the idler, reduces the maintenance workload and cost, prolongs the service life of the conveyor belt, reduces the deviation rate of the conveyor belt, and improves the operation reliability of the conveying equipment. Therefore, on the premise of ensuring the reliability of the design, the design of appropriate roller spacing can not only reduce the number of rollers, but also reduce the investment cost of the belt conveyor.
Due to the different tension and load of each point, the maximum allowable roller spacing of the belt conveyor is not the same, and the idler is arranged at equal intervals without considering the specific situation of each conveyor part, so the use of different roller spacing on the same belt conveyor is more in line with the actual use of the belt conveyor. Unequal spacing of belt conveyors can effectively reduce conveyor investment costs.
Methods for determining the spacing of idlers of belt conveyors:
As one of the core components of the belt conveyor, the idler is eventually installed in a variety of conveying equipment. The installation of conveyor rollers requires the calculation of the spacing of the rollers. So how to determine the roller spacing of a belt conveyor? The spacing of the idler should be designed to consider the sag of the conveyor belt, the bearing capacity of the roller bearing, such as the nature of the material, the width of the conveyor belt, the inclination angle of the conveyor, the actual operation and other factors. The following details the method of determining the spacing of the idler roller of the belt conveyor:
1) Bulk material conveyor roller spacing selection:
The belt conveyor used for transporting bulk materials has a roller spacing of about 0.8-1.5m for the load-bearing branch and about 2-3m for the return branch.
2) Long-distance belt conveyor roller spacing selection:
For long-distance belt conveyors, foreign countries usually adopt the method of increasing the spacing of idlers to reduce the total resistance. The spacing of the upper branch rollers can be increased to 2.5~5.0m, and the spacing of the lower branch rollers can be increased to 5~10m. However, this design is based on sufficient dynamic analysis to ensure reliable conveyor operation.
3) Selection of idler spacing of belt conveyor for finished items:
Generally speaking, when conveying finished items with a weight greater than 20kg, the roller spacing should not be greater than 1/2 of the length of the article (along the conveying direction), and the roller spacing for finished items below 20kg can be taken as 1m.
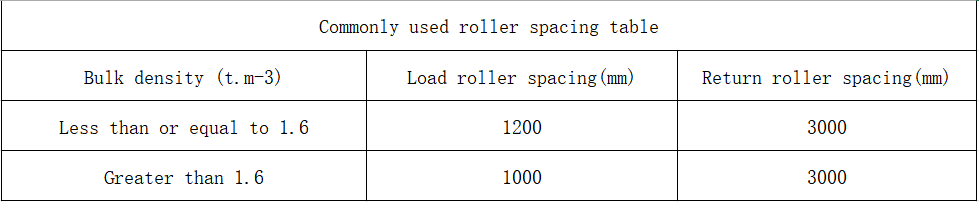
Commonly used roller spacing table for load-bearing rollers and return rollers:


Previous: The Key Role And Application Of Aluminum Guide Rollers in Textile Machinery
Next: What Data Do I Need To Provide To The Manufacturer For Custom Banana Guide Rollers?